World's river deltas sinking due to human activity – Radiocápsula RCP/CPR
Submitted on 20 September 2009 - 6:22pm
This article is reproduced by CienciaPR with permission from the original source.
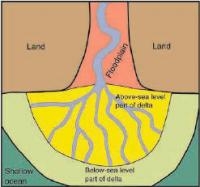
Eurekalert - A new study led by the University of Colorado at Boulder indicates most of the world's low-lying river deltas are sinking from human activity, making them increasingly vulnerable to flooding from rivers and ocean storms and putting tens of millions of people at risk.
While the 2007 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report concluded many river deltas are at risk from sea level rise, the new study indicates other human factors are causing deltas to sink significantly. The researchers concluded the sinking of deltas from Asia and India to the Americas is exacerbated by the upstream trapping of sediments by reservoirs and dams, man-made channels and levees that whisk sediment into the oceans beyond coastal floodplains, and the accelerated compacting of floodplain sediment caused by the extraction of groundwater and natural gas.
The study concluded that 24 out of the world's 33 major deltas are sinking and that 85 percent experienced severe flooding in recent years, resulting in the temporary submergence of roughly 100,000 square miles of land. About 500 million people in the world live on river deltas.
Published in the Sept. 20 issue of Nature Geoscience, the study was led by CU-Boulder Professor James Syvitski, who is directing a $4.2 million effort funded by the National Science Foundation to model large-scale global processes on Earth like erosion and flooding. Known as the Community Surface Dynamic Modeling System, or CSDMS, the effort involves hundreds of scientists from dozens of federal labs and universities around the nation.
The Nature Geoscience authors predict that global delta flooding could increase by 50 percent under current projections of about 18 inches in sea level rise by the end of the century as forecast by the 2007 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report. The flooding will increase even more if the capture of sediments upstream from deltas by reservoirs and other water diversion projects persists and prevents the growth and buffering of the deltas, according to the study.
"We argue that the world's low-lying deltas are increasingly vulnerable to flooding, either from their feeding rivers or from ocean storms," said CU-Boulder Research Associate Albert Kettner, a co-author on the study at CU-Boulder's Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research and member of the CSDMS team. "This study shows there are a host of human-induced factors that already cause deltas to sink much more rapidly than could be explained by sea level alone."
Other study co-authors include CU-Boulder's Irina Overeem, Eric Hutton and Mark Hannon, G. Robert Brakenridge of Dartmouth College, John Day of Louisiana State University, Charles Vorosmarty of City College of New York, Yoshiki Saito of the Geological Survey of Japan, Liviu Giosan of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute and Robert Nichols of the University of Southampton in England.
The team used satellite data from NASA's Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, which carried a bevy of radar instruments that swept more than 80 percent of Earth's surface during a 12-day mission of the space shuttle Endeavour in 2000. The researchers compared the SRTM data with historical maps published between 1760 and 1922.
"Every year, about 10 million people are being affected by storm surges," said CU-Boulder's Overeem, also an INSTAAR researcher and CSDMS scientist. "Hurricane Katrina may be the best example that stands out in the United States, but flooding in the Asian deltas of Irrawaddy in Myanmar and the Ganges-Brahmaputra in India and Bangladesh have recently claimed thousands of lives as well."
The researchers predict that similar disasters could potentially occur in the Pearl River delta in China and the Mekong River delta in Vietnam, where thousands of square miles are below sea level and the regions are hit by periodic typhoons.
"Although humans have largely mastered the everyday behaviour of lowland rivers, they seem less able to deal with the fury of storm surges that can temporarily raise sea level by three to 10 meters (10 to 33 feet)," wrote the study authors. "It remains alarming how often deltas flood, whether from land or from sea, and the trend seems to be worsening."
"We are interested in how landscapes and seascapes change over time, and how materials like water, sediments and nutrients are transported from one place to another," said Syvitski a geological sciences professor at CU-Boulder. "The CSDMS effort will give us a better understanding of Earth and allow us to make better predictions about areas at risk to phenomena like deforestation, forest fires, land-use changes and the impacts of climate change."
Contact: Albert Kettner
kettner@colorado.edu
303-735-5486
University of Colorado at Boulder







